Key Things to Know About Matchmaking
Before setting up your event, it’s important to know these key points about how matchmaking works:
Driven by product categories
Takes into account ALL objects on the platform (people, products, exhibiting companies, speakers, sessions, news, webinars, etc.)
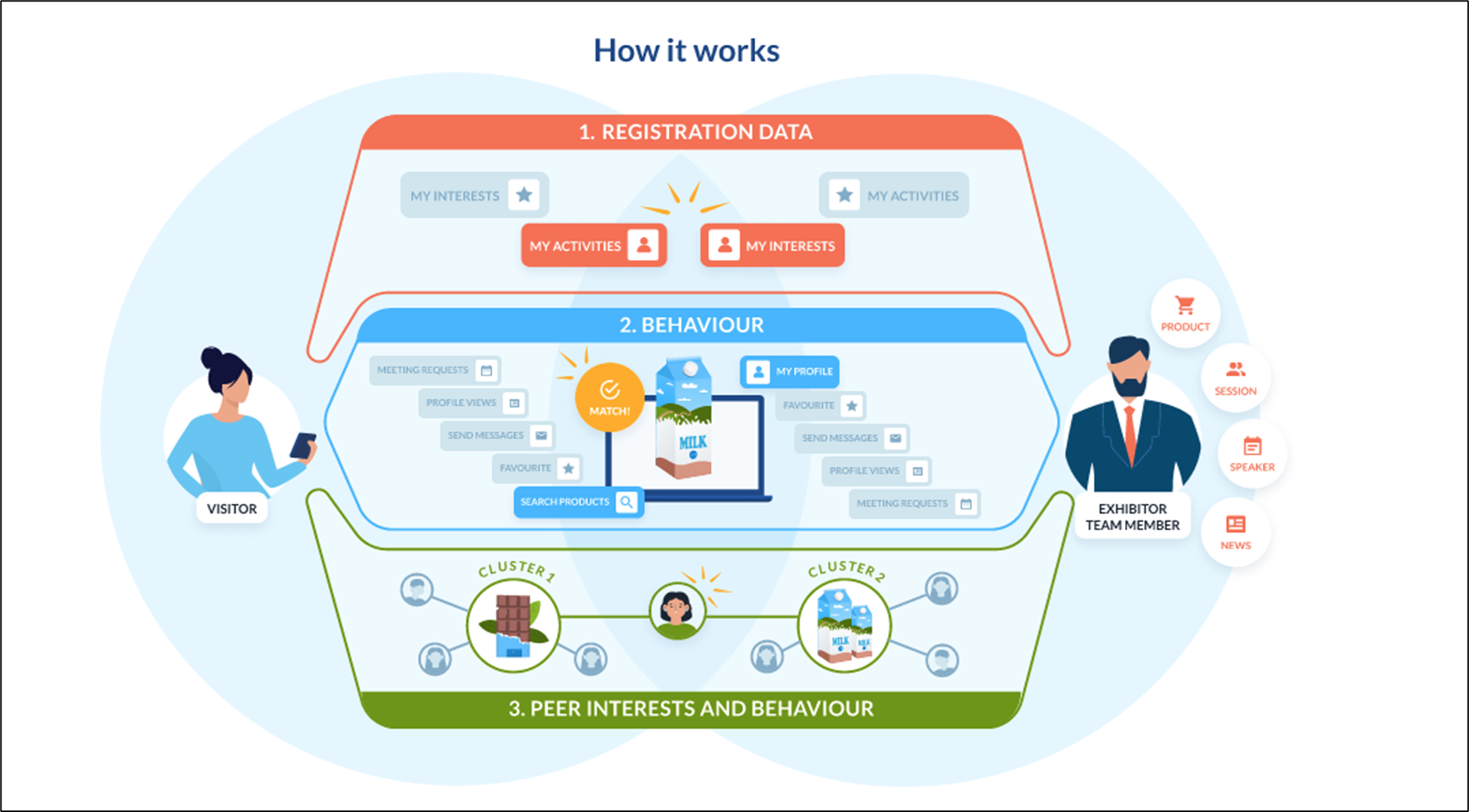
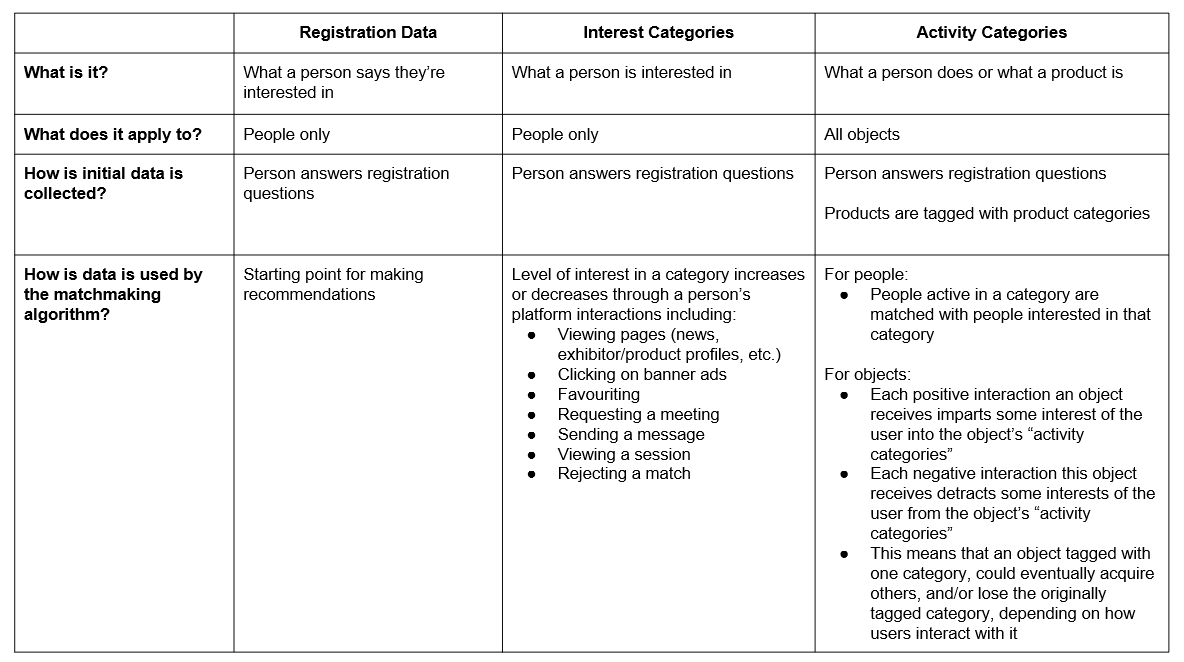
Matchmaking algorithm explained:- The matching algorithm is initialised using registration data. - It learns over time based on user behaviour - interactions between users. - It uses information from peer interests and behaviour that influences recommendations for the user
Categories are used in two ways:
Activity categories - These categories define what exhibitors or visitors do or their specific roles or activities. It describes their participation or involvement at the event.
Interest categories - These categories define what exhibitors or visitors are seeking or interested in. It reflects their preferences or what they are looking for at the event.
Therefore, matchmaking works by connecting "interest" categories to "activity" categories for exhibitors and visitors.
Each person has a different level of interest in each product category (it’s not just “yes” or “no”)
All objects on the platform (people, products, sessions, exhibitors, etc.) are tagged by one or more product categories
The system recommends things to you that best match your current interests, which can change over time
Example:
Visitor A is interested in apples
She indicates this by choosing product category apples as her interest in the registration question that asks about her interests
Exhibitor 1 sells apples
He indicates this by tagging his company with product category apples
He also indicates this by choosing product category apples as his activity in Edit Profile in his team member profile
Results
Exhibitor 1’s company is recommended to Visitor A (product category based recommendation)
Exhibitor 1’s team member profile is recommended as a match for Visitor A (activity to interest match)
Visitor A is recommended to Exhibitor 1 (interest to activity match)
How matches and recommendations are made:
Recommendations are specific to a person and are often unique to that person
Recommendations combine peer interests and product category interests to create a ranked list of all objects in the system
Matchmaking filters can be used to eliminate matches in the ranked list between specific people and/or companies based on answers to registration questions (e.g. small buyer should not match with large supplier)
Items that are at the top of the ranked list for their respective types (e.g. products, people, exhibitors, etc.) are then shown as recommendations to the person
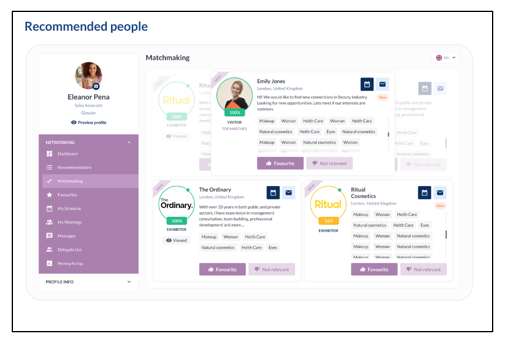
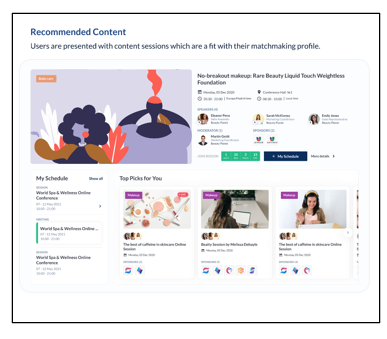
How matches and recommendations evolve over time:
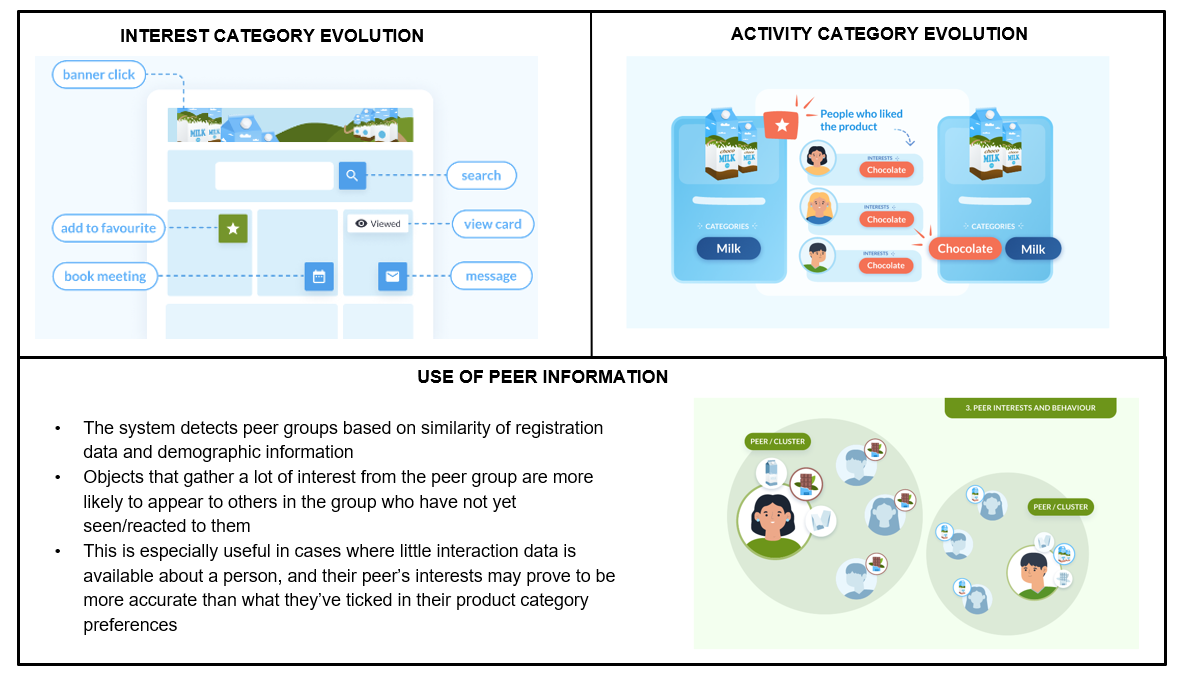
Set up Best Practices:
Include both interest and activity questions for all registration categories, including team members
Important note, if an interest or activity category question is not included, then the system copies information from the existing question and uses this information for the missing item.
Example, an interest question is asked but not an activity question so the system takes the interest answers and uses those as activity answers. This means the person now has incorrect activity answers and will receive incorrect matches as a result.
Leverage matchmaking filters to eliminate unwanted matches
Where it makes sense, use data matching to help refine recommendations
You can hide matchmaking for a specific participant category, from Registration Settings → Visitor → Participants Category, To Read More Click Here
